What are Deep Foundations?
deep foundation is needed to carry loads at depth or for functional reasons from a structure through weak compressible soils or fills on to stronger and less compressible soils or rocks.
Deep foundations under the finished ground surface are founded too deeply for their base bearing ability to be affected by surface conditions, generally at depths > 3 m below the finished ground level.
When unsuitable soils are present near the surface, the deep foundation may be used to transfer the load to a deeper, more capable strata at depth.
Types of Deep Foundation
The types of deep foundations in general use are as follows:
- Basements
- Buoyancy rafts (hollow box foundations)
- Caissons
- Cylinders
- Shaft foundations
- Pile foundations
1. Basement foundation
They are hollow https://y4c.com/soma-medication/ substructures built to provide space below ground level for the work or storage. The structural design is driven by its practical needs rather than by considerations of the most effective method of resisting external earth and hydrostatic pressures. In open excavations, they are set up in place.
2. Buoyancy Rafts (Hollow Box Foundations)
Buoyancy rafts are hollow substructures designed to provide a buoyant or semi-buoyant substructure underneath which reduces net loading to the desired low intensity on the soil. Buoyancy rafts can be constructed to be sunk as caissons, and can also be installed in open excavations.
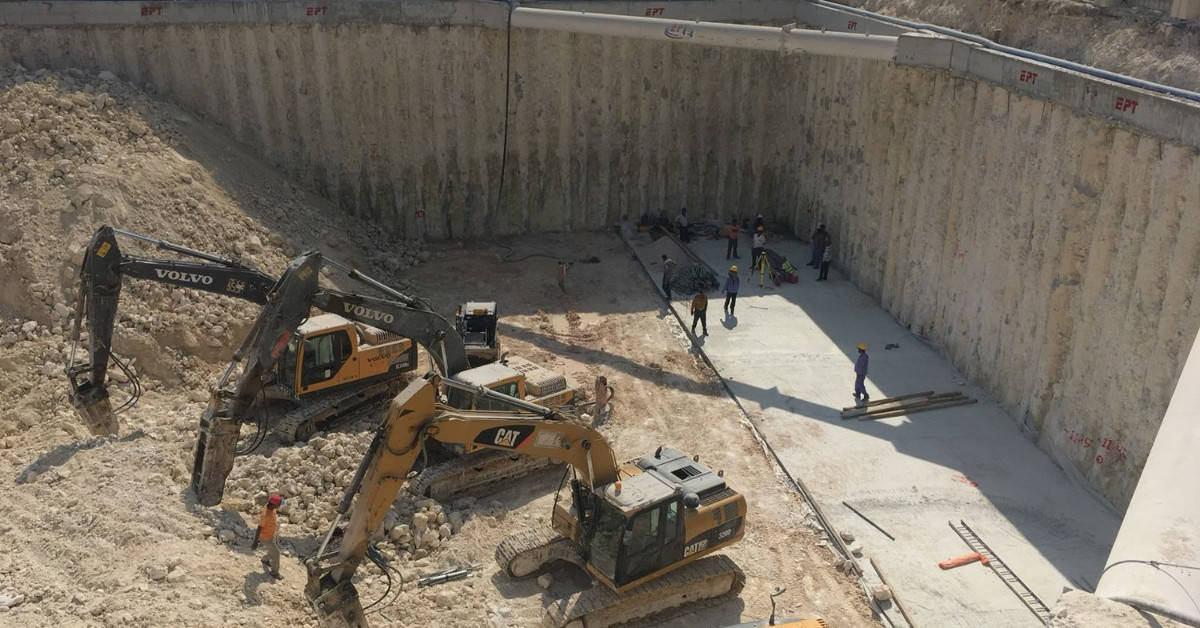
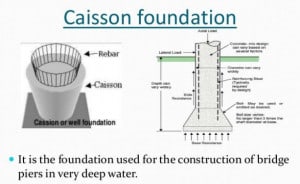
3. Caissons Foundations
Caissons are hollow substructures designed to be constructed on or near the surface and then sunk as a single unit to their required level.
4. Cylinders
Cylinders are small single-cell caissons.
5. Drilled Shaft foundations
Shaft foundations are constructed within deep excavations supported by lining constructed in place and subsequently filled with concrete or other pre-fabricated load-bearing units.
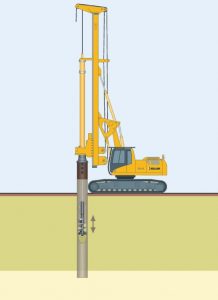
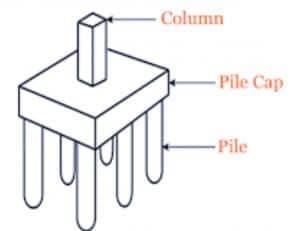
6. Pile foundations
Pile foundations are relatively long and slender members designed by driving preformed units to the desired foundation level, or by driving or drilling in tubes to the appropriate depth – tubes filled with concrete before or during withdrawal or by drilling unlined or wholly or partially lined boreholes filled with concrete after that.