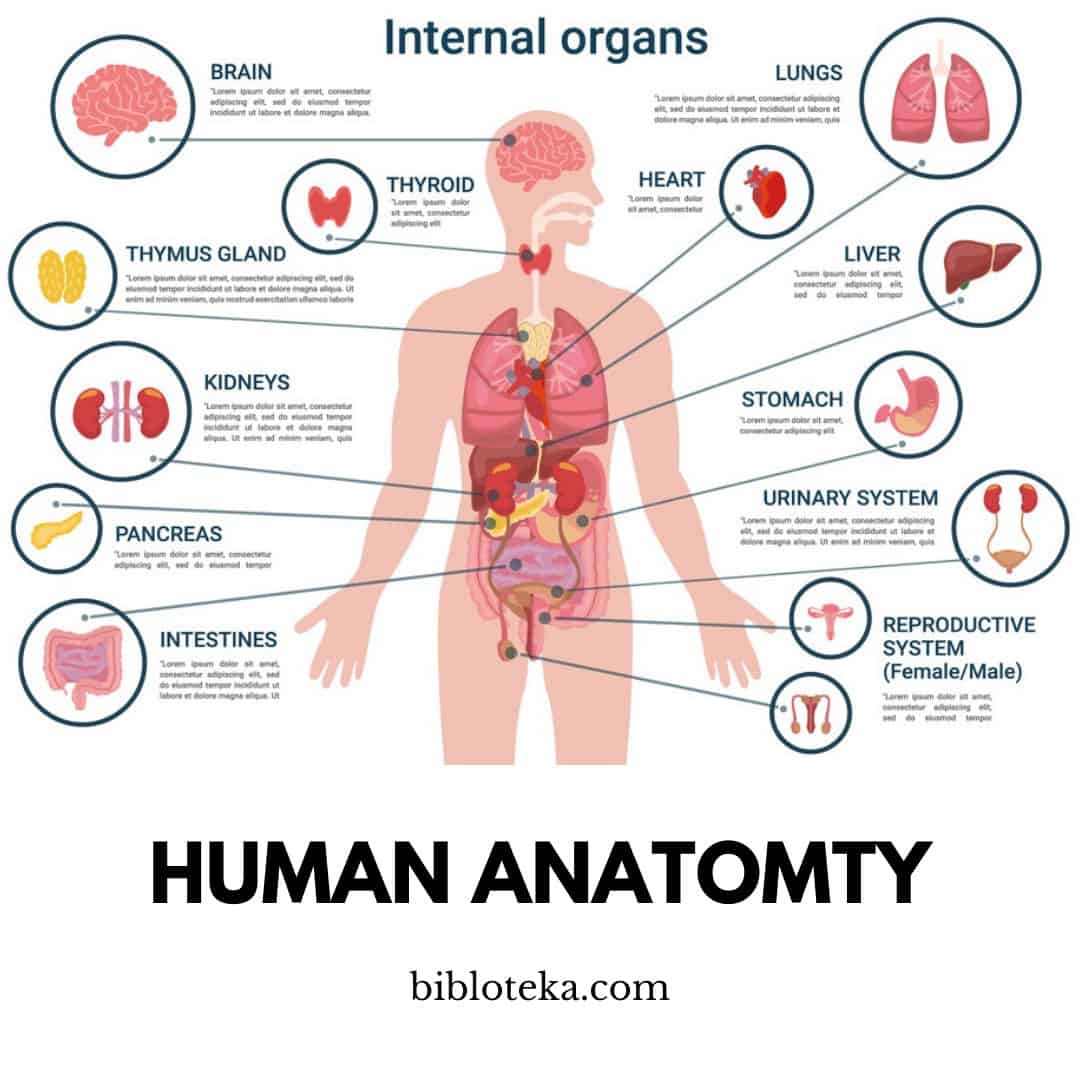
To survive and reproduce, the human body depends on important bodily organs to perform certain vital functions. When two or more organs together with their associated structures work together they become components of a body system.
The number of organs that the human body has is twenty – one, and each one of them fulfills a fundamental and important function for the proper functioning of the organism. The structure of the organs varies according to the case, being smaller or bigger according to the functions that it must have in the body, and the eventual storages that it will have to do.
Physically, however, the organs are classified between the solid ones (which have an inner and an outer part) and the membranous or hollow ones (which have the morphology of the hollow sac).
What is an organ?
The organs of the human body are collections of tissues that perform a specific function in the system. It is an anatomical and functional unit, that is, a series of tissues that perform various functions together.
In other words, organs are units of our body well differentiated from other tissues in our body. These tissues that make up the structure in turn are made up of specialized cells.
These sets of tissues thus perform a series of irreplaceable specific vital functions. In addition, there are closely related organs, acting at the level of what is known as systems.
The different organs then interact with each other to reach one or more functional purposes for the human body. We can then speak of systems such as the digestive system, made up of organs such as the stomach, pancreas, liver, or small intestine.
Anyway, there are relationships at an integral level in our body. For example, the nervous system is related to each and every other system in our body.
It is very important to note that all organs are essential for our survival. There are only a few very specific cases in which you can survive without one of them.
What are Internal organs?
All organs of the human body not visible externally are called internal organs.
The internal organs constitute the most conspicuous part of the organs of the human body; among the internal organs of the human body, the following deserve a mention: the brain, the cerebellum, the brain stem, the spinal cord, the cranial and spinal nerves, the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, the heart, the lungs, the liver, the kidneys, adrenals, stomach, intestines, pancreas, bladder, spleen, thyroid, parathyroid glands, bones, bone marrow, and muscles. It should be noted that there are organs in the human body that are partly internal and partly external; these bodies, therefore, belong both to the category of internal organs and to the category of external organs.
Important organs of the human body with the above characteristics are the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth.
1.Heart
The heart is the main organ of the circulatory system.
Its function is to pump blood to the rest of the tissues and organs of the human body through the bloodstream. It is located in the thoracic cavity towards the left side.
It is made up of a sac that we call the “pericardium”, in charge of giving flexibility and mobility to this muscle. In turn, the pericardium is divided into a fibrous and a serious part. The latter consists of three layers: the epicardium, the myocardium, and the endocardium.
Finally, the heart is made up of four chambers, two of them superior, which we call the right and left atrium; and two inferior ones, which we know as the right and left ventricles and the muscles moves by two types of movements:
Systole: the heart drives the blood to ensure that oxygen reaches the entire body
Diastole: is when you relax and receive blood from the tissues
The movement of systole and diastole is what is known as the cardiac cycle and is what allows oxygen to be pumped.
2.Lungs
Within the chest is of the human body are also the lungs, organs that are part of the respiratory system, and in the center of which is the heart. Both vital organs are protected by the ribs.
The lungs allow us to breathe, that is, to inhale the air and oxygen in the atmosphere, but it also provides us with a lesser-known function and it is the one that produces mucus to prevent inhaled germs from attacking our health.
3.Liver
The liver is an organ of the human body involved in numerous important functions; These functions include:
The production of essential proteins and hormones;
The regulation of carbohydrate metabolism (in particular it directs the processes of gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, and glycogenosynthesis);
The production of bile, a liquid containing water, electrolytes, lipids, proteins, and pigments that has a pivotal role in the digestive process (provides for the digestion of fats );
The generation of coagulation factors;
The regulation of cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood;
The elimination from the blood of the so-called waste products, which can be: toxins, infectious agents and catabolites (e.g. ammonia );
The infusion of new energy to the organism, when there is a general energy deficit.
4.Kidneys
They are two organs of the body located in the lower back or posterior area of the abdomen. Its main function is to filter the blood and help to eliminate the waste present in it.
There are filters in the kidneys that are called nephrons. When the blood has been filtered, its circulation continues. Meanwhile, the waste filtered by the kidneys will later be expelled through the urine.
The ureters are responsible for conducting the fluid with waste from the kidney to the bladder. When it fills up with fluid, the urine is expelled through the urethra. The kidney is responsible for the formation of urine.
5.Liver
The Liver is one of the vital internal organs of the human body. It is located on the right side of the abdomen. Its functions include the transformation of substances that are harmful to the body into other harmless substances. The liver also performs other functions such as the manufacture of bile, which is essential for digestion.
In addition to producing bile, the liver is important in the production of some proteins and in the detoxification of many organic molecules. It is also responsible for transforming part of the food into carbohydrates and is capable of manufacturing proteins.
6.Pancreas
It is an organ of the digestive system located in the right part of the abdomen. It is a gland that secretes substances called enzymes, necessary for the performance of the digestive function. Another major function of the pancreas as a gland is the production of hormones such as insulin. This serves to maintain adequate blood sugar levels. Diabetes may be due to a deficit in insulin production, which is handled by the pancreas.
7.Spleen
It is part of the lymphatic system. It is located in the upper left part of the abdomen. It is not a vital organ because it is possible to live without it, although the body would become more fragile in the face of infections. Among its functions is to filter blood and remove defective red blood cells from it. It is also in charge of producing antibodies that help defend against infections.
8.Stomach
It is an enlarged part of the digestive tract that can expand to accommodate the food that arrives there. The stomach accumulates, on average, two liters of food and liquid. It is responsible for secreting gastric juice, which contains enzymes that initiate the digestion of proteins. The bolus, after being mixed with gastric juice and undergoing the action of stomach movements, forms a viscous mass called chyme.
In the stomach, the food suffers the action of gastric juice.
9.Small intestine
It is the longest compartment of the digestive system, reaching about six meters in length.
The initial section of the small intestine is called the duodenum. This is a C-shaped fold of the intestine that houses the main duodenal papilla that receives secretions from the biliary system.
The duodenum connects to the jejunum. This constitutes two-thirds of the small intestine and has a large lumen. It has numerous folds on its internal surface and is the location of most absorption of nutrients and minerals.
The ileum is the last part of the small intestine. This is a narrower and longer section of the small intestine (forms the remaining two thirds).
The ileum is where most of the fat absorption occurs. The ileum ends at the ileo-cecal junction, which acts as a valve and prevents the reflux of the cecum. The terminal ileum is where vitamin B12 and bile salts are absorbed.
It is in the small intestine that most of the enzymatic breakdown of macromolecules occurs and much of the absorption of nutrients. In this organ, the food will undergo the action of pancreatic bile secretions and its own secretions. In the small intestine, much of the digestion takes place.
10.Large intestine
It receives this name for having a larger diameter than the small intestine. This organ performs as the main function of the absorption of water and the formation of the fecal mass.
Feces are formed in the large intestine.
11.Bladder
It is a muscular and hollow organ responsible for the storage of urine until its elimination.
The bladder stores urine.
12.Uterus
Located inside the pelvic cavity, the uterus is a muscular, hollow, and elastic organ. He is responsible for menstruation, pregnancy, and childbirth.
Its main function is to shelter the fetus after fertilization.
13.Ovaries
The ovaries are two oval-shaped organs located in the pelvic cavity of women.
Its function is based on the production of the female hormone, estrogen, as well as the production of eggs, the female sexual gametes.
14.Prostate
It is a gland present in man that has the function of secreting a neutralizing component of sperm acids. The prostate surrounds a portion of the urethra, which is called the prostatic urethra. When there is an enlargement of the prostate, obstruction of the urethra may occur.
The prostate produces the secretion that forms the sperm.
15.Testicles
They are the male gonads in which sperm are produced. In addition to this function, the testicles are responsible for the production of testosterone, a sex hormone. The testicle produces sperm and testosterone.
16.Brain
It is a portion of the central nervous system related to a number of functions. Among the functions exercised by the brain are the control of skeletal muscle contraction, learning, emotion, and memory. This organ has two hemispheres – left and right – and two regions – white and gray substances. The white matter is more internally arranged, while the gray matter is more externally arranged.
It is the largest organ in our nervous system and is in charge of controlling all the impulses that are distributed throughout the body. Neurons are the nerve connections responsible for processing information and allowing brain activity to proceed normally; These elements communicate with each other by connecting fibers.
The brain fulfills these main functions :
- Produces hormones and releases them
- Process the information we receive through the senses
- It is in charge of controlling the movement of our muscles
- Thanks to his activity we can reason, memorize, and learn.
17.Thymus
The thymus is a glandular organ that belongs to the immune system. Its main function is to give the body adaptability in front of external invading microorganisms. that is why different lymphocytes mature within the thymus, among which T-cells stand out.
See Also