Before deciding on a new strategy, conduct a SWOT Analysis to assess your organization’s current position.
Find out what works well and what doesn’t. Consider where you want to go, how you might get there – and what might get in your way. These are big issues, and you’ll need a powerful but simple technique to help you: SWOT Analysis.
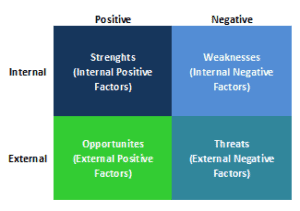
What is SWOT Analysis?
The term “SWOT analysis” relates to the framework for evaluating a company’s competitive position and drawing upon the strengths, weaknesses, and threats of a strategic plan.
SWOT analysis is a useful technique for internal and external scanning where strengths and weaknesses are derived from an internal environment, while external environmental opportunities and threats arise.
It helps to match the company’s resources and capabilities to the competitive environment in which it operates.
When should you perform a SWOT analysis?
You can employ a SWOT analysis before you commit to any sort of company action, whether you are exploring new initiatives, revamping internal policies, considering opportunities to pivot or altering a plan midway through its execution.
Sometimes it’s wise to perform a general SWOT analysis just to check on the current landscape of your business so you can improve business operations as needed. The analysis can show you the key areas where your organization is performing optimally, as well as which operations need adjustment.
Don’t make the mistake of thinking about your business operations informally, in hopes that they will all come together cohesively. By taking the time to put together a formal SWOT analysis, you can see the whole picture of your business. From there, you can discover ways to improve or eliminate your company’s weaknesses and capitalize on its strengths.
While the business owner should certainly be involved in creating a SWOT analysis, it is often helpful to include other team members in the process. Ask for input from a variety of team members and openly discuss any contributions made. The collective knowledge of the team will allow you to adequately analyze your business from all sides.
Who should do a SWOT Analysis?
For a SWOT analysis to be effective, company founders and leaders need to be deeply involved. This isn’t a task that can be delegated to others.
But, company leadership shouldn’t do the work on their own, either. For best results, you’ll want to gather a group of people who have different perspectives on the company. Select people who can represent different aspects of your company, from sales and customer service to marketing and product development. Everyone should have a seat at the table.
Innovative companies even look outside their own internal ranks when they perform a SWOT analysis and get input from customers to add their unique voice to the mix.
If you’re starting or running a business on your own, you can still do a SWOT analysis. Recruit additional points of view from friends who know a little about your business, your accountant, or even vendors and suppliers. The key is to have different points of view.
Existing businesses can use a SWOT analysis to assess their current situation and determine a strategy to move forward. But, remember that things are constantly changing and you’ll want to reassess your strategy, starting with a new SWOT analysis every six to 12 months.
For startups, a SWOT analysis is part of the business planning process. It’ll help codify a strategy so that you start off on the right foot and know the direction that you plan to go.
Components of SWOT Analysis in Business
1. Strengths
Strengths in SWOT analysis are the attributes in an organization which is considered necessary for a project’s ultimate success. For the competitive advantage, strengths are resources and capabilities. For example, Apple has a high brand value and an extremely loyal client base whereas Samsung has a broad variety of products which cater to high-end and low-budget mobile phones. Examples of strengths frequently mentioned include:
- Brands with strong names
- Good reputation
- Cost benefits of own know-how
2. Weaknesses
Weaknesses are the factors in the SWOT analysis formula which can stop effective project outcomes. Weaknesses include factors such as abundant rivalries between different departments, weak internal communication systems, insufficient funding, and insufficient materials.
For example, a lack of capital is a significant weakness for most small company owners. In the inner view and from a business point of view the weaknesses of an organization can also be seen. Additional weaknesses are:
- Weak brand name
- Poor reputation
- Inefficient and costly structure
3. Opportunities
Opportunities are categorized as external components that can help achieve the project objectives. Those factors can affect vendors wanting to work together to assist the business to succeed, the general public’s positive perception of the business and the market conditions to make the project suitable for one market segment. Other opportunities include:
- New technology arrival
- Customer demands not met
- Training
4. Threats
This SWOT analysis category refers to the factors that could hurt an organization’s reputation or performance. They are external factors that are not under the control of an organization, but they can consider implementing a contingency plan to a certain extent in order to reduce its impact. For example, drought presents a major threat to any agricultural industry, which could decrease or harm crop yield entirely. There are also other threats:
- Trend changes
- New substitute products
- New regulations
Advantages of SWOT Analysis in Business
- It includes multi-level analysis which gives useful data on an organization, taking into consideration each of the four SWOT analysis elements.
- It may be used to establish strategic planning objectives for an organization, an individual or a team.
- It does not require technical skills or training but can be carried out by everyone who is familiar with the company.
- It is also a low-cost technique because an external highly paid consultant is not required.
- It can assist to identify an organization’s core competences.
- It can assist to understand the past, present, and future by means of past and current data.
Disadvantages of SWOT Analysis in Business
- It makes every factor one-dimensional, classifying it as strength, weakness, opportunity or threat. Therefore, every attribute or factor obviously only affects the issue being analyzed in one dimension.
- Since the factors have no weight, no mechanism can provide for the importance of one factor over others. As such, the true impact of any factor on the overall objective is very hard to ascertain.
Recommended: Advanced PMP Questions and Answers